工厂方法模式和简单工厂模式的区别在于,简单工厂模式只有一个工厂,工厂方法模式对每一个产品都有相应的工厂。
工厂方法模式是简单工厂模式的衍生,解决了很多简单工厂模式的问题。
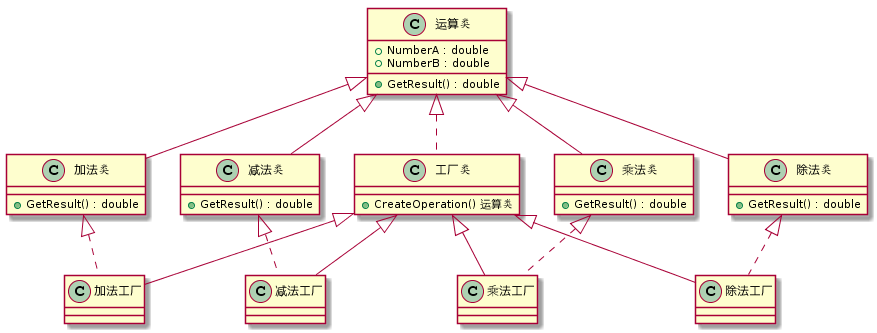
首先完全实现“开-闭”原则,实现了可扩展。其次更复杂的层次结构,可以应用于产品结果复杂的场合。
工厂方法模式对简单工厂模式进行了抽象。有一个抽象的Factory类(可以是抽象类和接口),这个类将不再负责具体的产品生产,而是只制定一些规范,具体的生产工作由子类去完成。在这个模式中,工厂类和产品类往往可以依次对应。即一个抽象工厂对应一个抽象产品,一个具体工厂对应一个具体产品,这个具体的工厂就负责生产对应的产品。
工厂方法模式(Factory Method Pattern)是最典型的模板方法模式(Template Method Pattern)应用
优点: 增加一个运算类(例如N次方类),只需要增加运算类和相对应的工厂,两个类,不需要修改工厂类。
缺点: 增加运算类,会修改客户端代码,工厂方法只是把简单工厂的内部逻辑判断移到了客户端进行。
# coding:utf-8
class AbstractSchool(object):
name = ''
addr = ''
principal = ''
def enroll(self, name, course):
raise NotImplementedError
def info(self):
raise NotImplementedError
class AbstractCourse(object):
def __init__(self, name, time_range, study_type, fee):
self.name = name
self.time_range = time_range
self.study_type = study_type
self.fee = fee
def enroll_test(self):
"""
参加这门课程前需要进行的测试
:return
"""
print("课程[%s]测试中..." % self.name)
def print_course_outline(self):
"""
打印课程大纲
:return:
"""
pass
class LinuxOPSCourse(AbstractCourse):
"""Linux运维课程"""
def print_course_outline(self):
outline = """
Linux 基础
Linux 基本服务使用
Linux 高级服务篇
Linux Shell 编程
"""
print(outline)
def enroll_test(self):
print("不用测试,是个人就能学...")
class PythonCourse(AbstractCourse):
"""Python 自动化开发课程"""
def print_course_outline(self):
outline = """
Python 介绍
Python 基础语法
Python 函数式编程
Python 面向对象
Python 网络编程
Python Web 开发基础
"""
print(outline)
def enroll_test(self):
print("------ Python 入学测试 ------")
print("------ 500 道题答完了 ------")
print("------ 通过了 ------")
class BJSchool(AbstractSchool):
name = "老男孩北京校区"
def create_course(self, course_type):
if course_type == 'py_ops':
course = PythonCourse("Python 自动化开发", 7, "面授", 11000)
elif course_type == 'linux':
course = LinuxOPSCourse("Linux 运维课程", 5, "面授", 12800)
return course
def enroll(self, name, course):
print("开始为新学员[%s]办入学手续..." % name)
print("帮学员[%s]注册课程[%s]..." % (name, course.name))
course.enroll_test()
def info(self):
print("------ [%s] ------" % self.name)
class SHSchool(AbstractSchool):
name = "老男孩上海分校"
def create_course(self, course_type):
if course_type == 'py_ops':
course = PythonCourse("Python 自动化开发", 8, '在线', 6500)
elif course_type == 'linux':
course = LinuxOPSCourse('Linux 运维课程', 6, '在线', 8000)
return course
def enroll(self, name, course):
print("开始为新学员[%s]办入学手续..." % name)
print("帮学员[%s]注册课程[%s]..." % (name, course.name))
course.enroll_test()
def info(self):
print("------ [%s] ------" % self.name)
school1 = BJSchool()
school2 = SHSchool()
school1.info()
c1 = school1.create_course('py_ops')
school1.enroll('张三', c1)
school1.enroll('王五', c1)
school2.info()
c2 = school2.create_course('py_ops')
school2.enroll('李四', c2)